

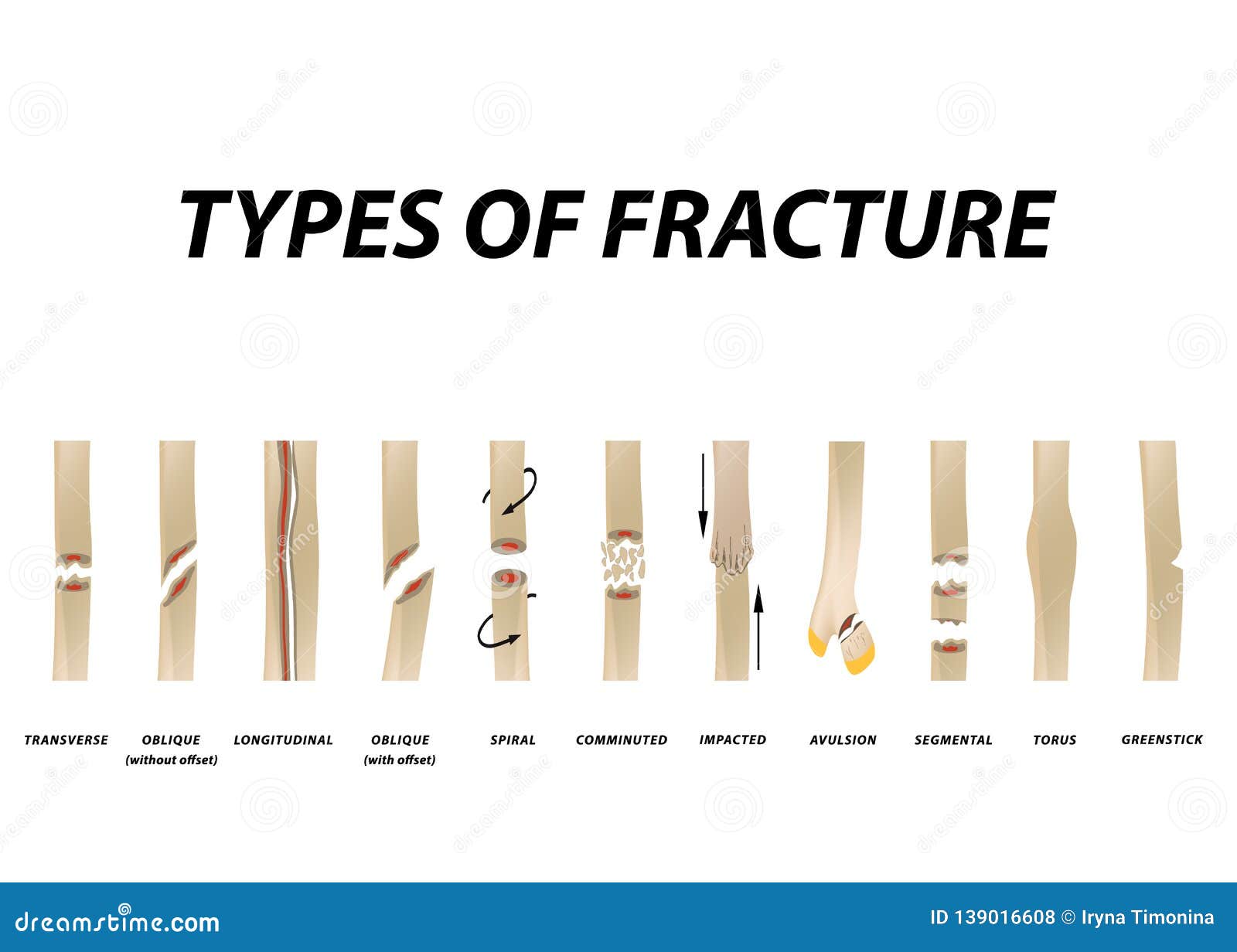
Therefore, fractures of the scapula are usually caused by high-energy trauma, such as a high-speed motor vehicle collision. Comminuted fracture: The bone breaks into several pieces, often requiring surgery.Fractures of the clavicle or the proximal humerus can be caused by a direct blow to the area from a fall, collision, or motor vehicle collision.īecause the scapula is protected by the chest and surrounding muscles, it is not easily fractured.Compression fracture – Where the bone is crushed, causing the broken portion to be wider or flatter in appearance.Stress fracture (hairline fracture): Tiny, hairline cracks form in the bone, usually caused by overuse or repetitive force in sports such as track and field or cross country running.Our physicians are extensively trained to treat growth plate fractures, ensuring that your child’s injured bone continues to grow and develop normally. These areas are weak and more likely to fracture. Growth plate fracture: Growth plates are the areas in children’s bones where growth happens.Other common pediatric fracture types include: Displaced fracture: The broken bone pieces are out of alignment and may require surgery to realign.Non-displaced fracture: The broken bone segments line up easily.Complex fractures are more serious and may require surgery. Open fracture (complex fracture): The bone breaks - sometimes into fragments- and damages the surrounding tissue, with possible tears through the skin.Spiral – The breakage spirals around the bone (often from a twisting injury).Transverse – A straight-line break across a bone.Oblique – A diagonal break across the bone.Simple fractures can usually be treated with nonsurgical procedures such as realigning and casting. Closed fracture (simple fracture): The bone breaks clean but doesn’t damage surrounding tissue or puncture the skin.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF BONE FRACTURE CRACK
Greenstick fracture: The bone is bent, with a crack on one side but intact on the other – similar to how a stick from a tree branch looks when you try to bend and break it.Īs bones mature, complete bone fractures - where the bone breaks into two or more pieces - are more likely.Buckle or torus fracture: Also know as an impacted fracture, it involves one side of the bone buckling on itself without breaking the other side.
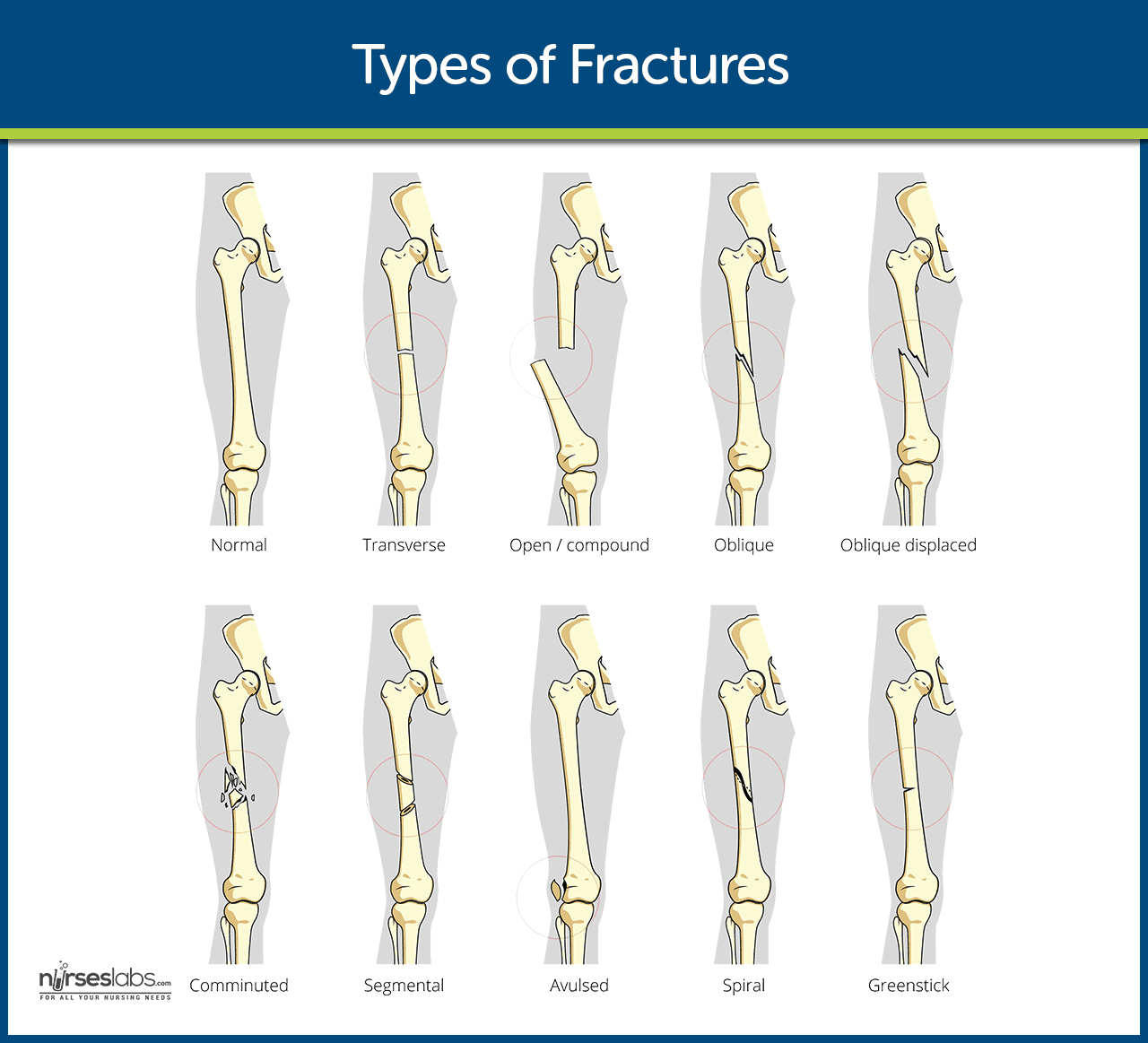
Most fractures in children are incomplete fractures, with the bone cracking or only partially breaking. What are the different types of Fractures? Complete fractures include: Still, forces applied to bones can be too strong, and the bones will indeed sometimes break, requiring medical treatment. At the Children’s Health, our pediatric orthopedic specialists have extensive training to diagnose and treat bone fractures with advanced, effective techniques that support your child’s skeletal growth and development. Their bones will buckle or bend before completely breaking. That’s because children’s bones are still growing, which makes them softer and more flexible. The younger your child, the faster healing will occur. The good news is that fractures in children tend to heal fast.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
